5 min read
Introducing tracing, multi-modal attachments, JSON streaming to clients, and more.
The Vercel AI SDK is a toolkit for building AI applications with JavaScript and TypeScript. Its unified API allows you to use any language model and provides powerful UI integrations into leading web frameworks such as Next.js and Svelte.
Vercel AI SDK 3.3 introduces four major features:
Tracing (experimental): instrument AI SDK functions using OpenTelemetry
Multi-Modal File Attachments (experimental): send file attachments with
useChatuseObject hook (experimental): stream structured object generation to the client
Additional LLM Settings: raw JSON for tools and structured object generation, stop sequences, and sending custom headers
We have also added AWS Bedrock and Chrome AI (community) model providers as well as many smaller features and additions. You can find all changes including minor features in our changelog.
Experimental features let you use the latest AI SDK functionality as soon as possible. However, they can change in patch versions. Please pin the patch version if you decide to use experimental features.
Link to headingTracing
Given the non-deterministic nature of language models, observability is critical for understanding and developing AI applications. You need to be able to trace and understand timing, token usage, prompts, and response content for individual model calls.
The Vercel AI SDK now supports tracing with OpenTelemetry, an open-source standard for recording telemetry information, as an experimental feature. Here is an example of how trace visualization looks with the Vercel Datadog integration:
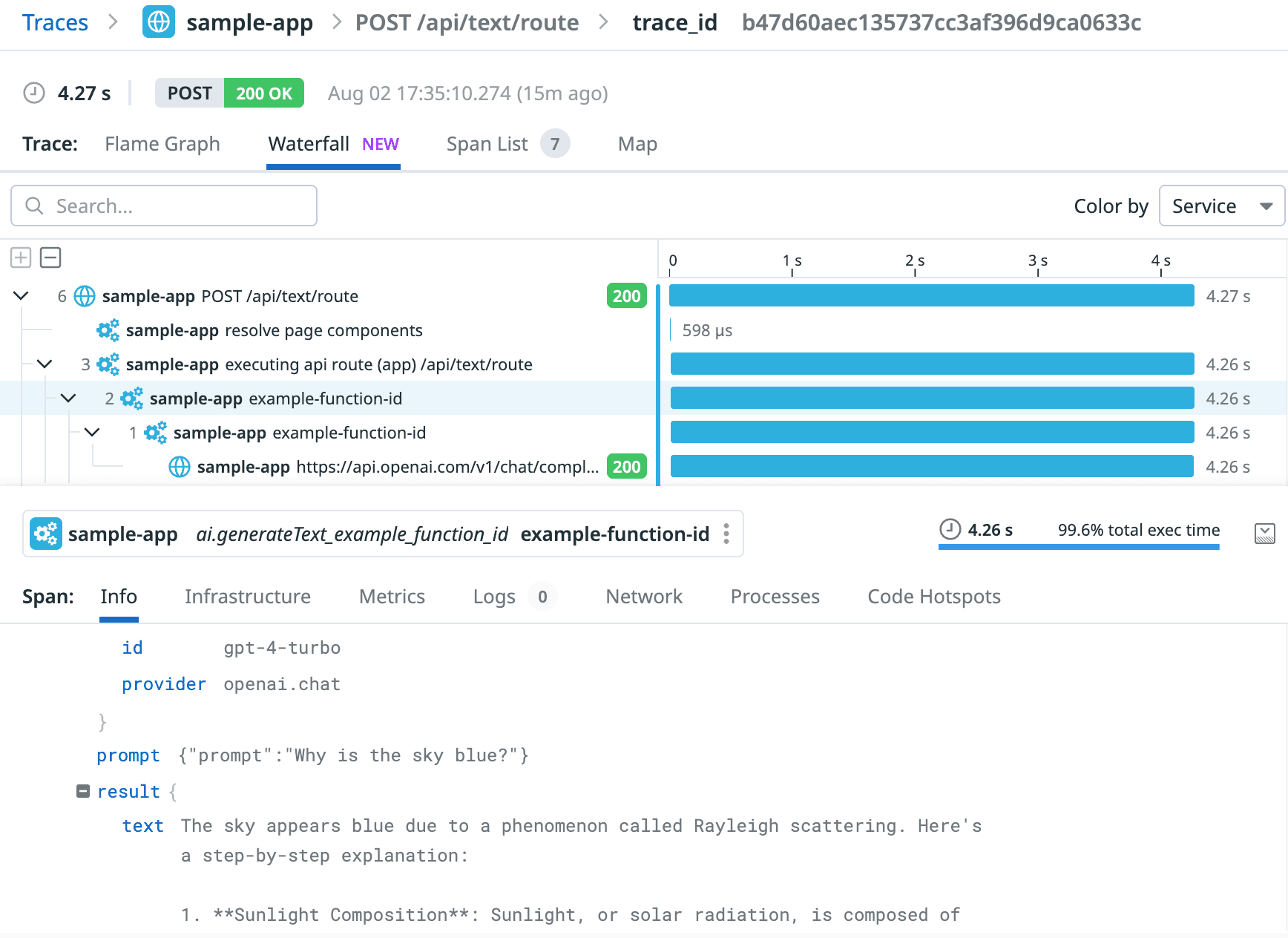
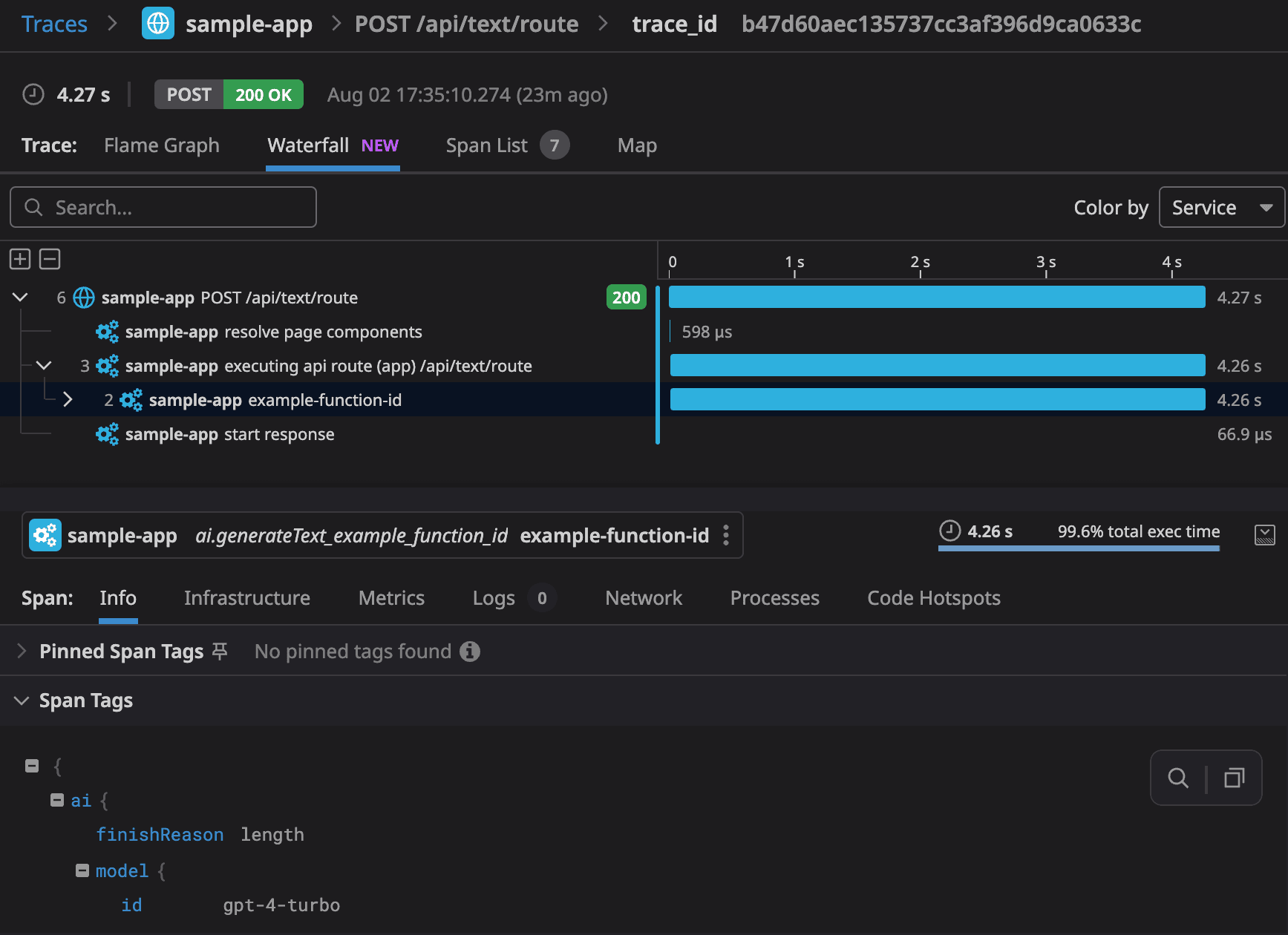
You can analyze the AI SDK tracing data with Vercel observability integrations such as Datadog, Sentry, and Axiom. Alternatively, you can use LLM observability providers such as LangFuse, Braintrust, or LangSmith.
To use telemetry with the Vercel AI SDK, you need to configure it for your application. We recommend using @vercel/otel . If you are using Next.js and deploy on Vercel, you can add instrumentation.ts with the following code to your project:
import { registerOTel } from '@vercel/otel';
export function register() { registerOTel({ serviceName: 'your-project-nameapp' });}Because the tracing feature is experimental, you need to opt-in to record information using the experimental_telemetry option. You can also supply function IDs to identify the call location as well as additional metadata that you want to record.
const result = await generateText({ model: anthropic('claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620'), prompt: 'Write a short story about a cat.', experimental_telemetry: { isEnabled: true, functionId: 'my-awesome-function', metadata: { something: 'custom', someOtherThing: 'other-value', }, },});Enabling the feature will record tracing data for your function calls. You can find more details in the AI SDK telemetry documentation. If you want to get started, check out our deployable AI SDK Next.js tracing template.
Link to headingMulti-Modal File Attachments
In many AI chat applications, users need to send attachments along with their messages, such as images, PDFs, and various media files. These attachments also need to be available for preview alongside messages to be viewed by users.
As a result, we have added experimental_attachments to the handleSubmit() handler of the useChat() React hook.
Check out this example in action and deploy the template.
There are two ways to send attachments with a message, either by providing a FileList object or a list of URLs to the handleSubmit function:
Link to headingFileList
By using FileList, you can send multiple files as attachments along with a message using the file input element. The useChat hook will automatically convert them into data URLs and send them to the AI provider.
const { input, handleSubmit, handleInputChange } = useChat();const [files, setFiles] = useState<FileList | undefined>(undefined);
return ( <form onSubmit={(event) => { handleSubmit(event, { experimental_attachments: files, }); }} > <input type="file" onChange={(event) => { if (event.target.files) { setFiles(event.target.files); } }} multiple /> <input type="text" value={input} onChange={handleInputChange} /> </form>);Link to headingURLs
You can also send URLs as attachments along with a message. This can be useful for sending links to external resources or media content.
const { input, handleSubmit, handleInputChange } = useChat();const [attachments] = useState<Attachment[]>([ { name: 'earth.png', contentType: 'image/png', url: 'https://example.com/earth.png', }]);
return ( <form onSubmit={event => { handleSubmit(event, { experimental_attachments: attachments, }); }} > <input type="text" value={input} onChange={handleInputChange} /> </form>)You can learn more in our multi-modal chatbot guide.
Link to headinguseObject hook
Structured data generation is a common requirement in AI applications, e.g. for extracting information from natural language inputs. With the new useObject hook, you can stream structured object generation directly to the client. This experimental feature, available today for React, allows you to create dynamic interfaces that show JSON objects as they're being streamed.
For example, imagine an application where you can enter your expenses as text for reimbursement. You can use AI to convert textual inputs into structured objects, and stream the structured expense to the user as it’s being processed:
Here's how you could implement this in a Next.js application. First, define a schema for the expenses. The schema is shared between client and server:
import { z } from 'zod';
export const expenseSchema = z.object({ expense: z.object({ category: z .string() .describe( 'Category of the expense. Allowed categories: ' + 'TRAVEL, MEALS, ENTERTAINMENT, OFFICE SUPPLIES, OTHER.', ), amount: z.number().describe('Amount of the expense in USD.'), date: z .string() .describe('Date of the expense. Format yyyy-mmm-dd, e.g. 1952-Feb-19.'), details: z.string().describe('Details of the expense.'), }),});
export type PartialExpense = DeepPartial<typeof expenseSchema>['expense'];
export type Expense = z.infer<typeof expenseSchema>['expense'];Then, you use streamObject on the server to call the language model and stream an object:
import { anthropic } from '@ai-sdk/anthropic';import { streamObject } from 'ai';import { expenseSchema } from './schema';
// Allow streaming responses up to 30 secondsexport const maxDuration = 30;
export async function POST(req: Request) { const { expense }: { expense: string } = await req.json();
const result = await streamObject({ model: anthropic('claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620'), system: 'You categorize expenses into one of the following categories: ' + 'TRAVEL, MEALS, ENTERTAINMENT, OFFICE SUPPLIES, OTHER.' +
// provide date (including day of week) for reference: 'The current date is: ' + new Date() .toLocaleDateString('en-US', { year: 'numeric', month: 'short', day: '2-digit', weekday: 'short', }) .replace(/(\w+), (\w+) (\d+), (\d+)/, '$4-$2-$3 ($1)') + '. When no date is supplied, use the current date.', prompt: `Please categorize the following expense: "${expense}"`, schema: expenseSchema, onFinish({ object }) { // you could save the expense to a database here }, });
return result.toTextStreamResponse();}Finally, you consume the expense stream on a client page. While the expense is streaming, we preview the partial expense, and once the generation is finished, we append it to the list of expenses:
'use client';
import { experimental_useObject as useObject } from 'ai/react';import { Expense, expenseSchema, PartialExpense,} from '../api/expense/schema';import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Page() { const [expenses, setExpenses] = useState<Expense[]>([]);
const { submit, isLoading, object } = useObject({ api: '/api/expense', schema: expenseSchema, onFinish({ object }) { if (object != null) { setExpenses(prev => [object.expense, ...prev]); } }, });
return ( <div> <form onSubmit={e => { e.preventDefault(); const input = e.currentTarget.expense as HTMLInputElement; if (input.value.trim()) { submit({ expense: input.value }); e.currentTarget.reset(); } }} > <input type="text" name="expense" placeholder="Enter expense details"/> <button type="submit" disabled={isLoading}>Log expense</button> </form>
{isLoading && object?.expense && ( <ExpenseView expense={object.expense} /> )}
{expenses.map((expense, index) => ( <ExpenseView key={index} expense={expense} /> ))} </div> );}The expenses are rendered using an ExpenseView that can handle partial objects with undefined properties with .? and ?? (styling is omitted for illustration purposes):
const ExpenseView = ({ expense }: { expense: PartialExpense | Expense }) => ( <div> <div>{expense?.date ?? ''}</div> <div>${expense?.amount?.toFixed(2) ?? ''}</div> <div>{expense?.category ?? ''}</p></div> <div>{expense?.details ?? ''}</div> </div>);Check out this example in action and deploy the template.
You can use this approach to create generative user interfaces client-side for many different use cases. You can find more details on how to use it in our object generation documentation.
Link to headingAdditional LLM Settings
Calling language models is at the heart of the Vercel AI SDK. We have listened to your feedback and extended our functions to support the following features:
JSON schema support for tools and structured object generation: As an alternative to Zod schemas, you can now use JSON schemas directly with the
jsonSchemafunction. You can supply the type annotations and an optional validation function, giving you more flexibility especially when building applications with dynamic tools and structure generation.Stop sequences: Text sequences that stop generations have been an important feature when working with earlier language models that used raw text prompts. They are still relevant for many use cases, allowing you more control over the end of a text generation. You can now use the
stopSequencesoption to define stop sequences instreamTextandgenerateText.Sending custom headers: Custom headers are important for many use cases, like sending tracing information, enabling beta provider features, and more. You can now send custom headers using the
headersoption in most AI SDK functions.
With these additional settings, you have more control and flexibility when working with language models in the Vercel AI SDK.
Link to headingConclusion
With new features like OpenTelemetry support, useObject, and support for attachments with useChat, it’s never been a better time to start building AI applications.
Start a new AI project: Ready to build something new? Check out our multi-modal chatbot guide.
Explore our templates: Visit our Template Gallery to see the AI SDK in action and get inspired for your next project.
Join the community: Let us know what you’re building with the AI SDK in our GitHub Discussions.
We can't wait to see what you'll build next with Vercel AI SDK 3.3!
Link to headingContributors
Vercel AI SDK 3.3 is the result of the combined work of our core team at Vercel and many community contributors.
Special thanks for contributing merged pull requests:
gclark-eightfold, dynamicwebpaige, Und3rf10w, elitan, jon-spaeth, jeasonstudio, InfiniteCodeMonkeys, ruflair, MrMaina100, AntzyMo, samuelint, ian-pascoe, PawelKonie99, BrianHung, Ouvill, gmickel, developaul, elguarir, Kunoacc, florianheysen, rajuAhmed1705, suemor233, eden-chan, DraganAleksic99, karl-richter, rishabhbizzle, vladkampov, AaronFriel, theitaliandev, miguelvictor, jferrettiboke, dhruvvbhavsar, lmcgartland, PikiLee
Your feedback and contributions are invaluable as we continue to evolve the SDK.